
If an adding circuit is to compute the sum of three or more numbers, it can be advantageous to not propagate the carry result. Other adder designs include the carry-select adder, conditional sum adder, carry-skip adder, and carry-complete adder. For example, the following adder is a 64-bit adder that uses four 16-bit CLAs with two levels of lookahead carry units. This can be used at multiple levels to make even larger adders. See the simulation waveform below to understand what I just explained.The half adder adds two single binary digits A values for each block rather than each bit, and the carry-select adder which pre-generates the sum and carry values for either possible carry input (0 or 1) to the block, using multiplexers to select the appropriate result when the carry bit is known.īy combining multiple carry-lookahead adders, even larger adders can be created. This way we can add binary numbers of any size without mentioning the value of N specifically. After a pair of numbers are added, just apply reset for at least one clock cycle to show the end of inputs. And the cout output bit is considered to be valid only on the first clock cycle after a high reset. The cin bit is considered to be valid only on the first clock cycle after a low reset. And in each clock cycle we get the corresponding bit on output s. The design keeps adding the input bits in a serial way, when the reset is not high. Note that, even though this code works as a N-bit adder, we don't have to mention the value of N directly. generate clock with 10 ns clock period. If ( reset = 1 ) begin //active high resetĬ = cin //on first iteration after reset, assign cin to c.įlag = 1 //then make flag 1, so that this if statement isnt executed any more.Ĭ = ( a & b ) | ( c & b ) | ( a & c ) //CARRY

Output reg s, cout //note that s comes out at every clock cycle and cout is valid only for last clock cycle. Input a, b, cin, //note that cin is used for only first iteration. Note that we dont have to mention N here. Though I have used behavioral level approach to write my code, it should be straight forward to understand if you have the basics right. In this post, I have used a similar idea to implement the serial adder. The D flipflop is used to pass the output carry, back to the full adder with a clock cycle delay.
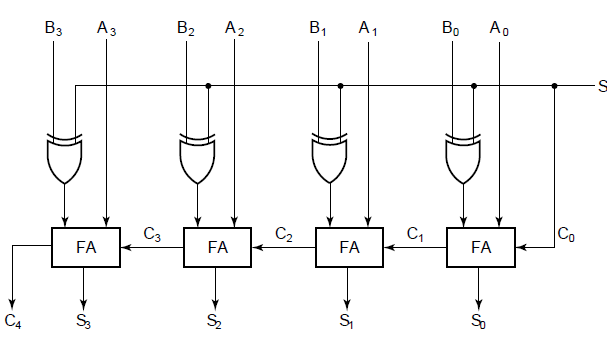
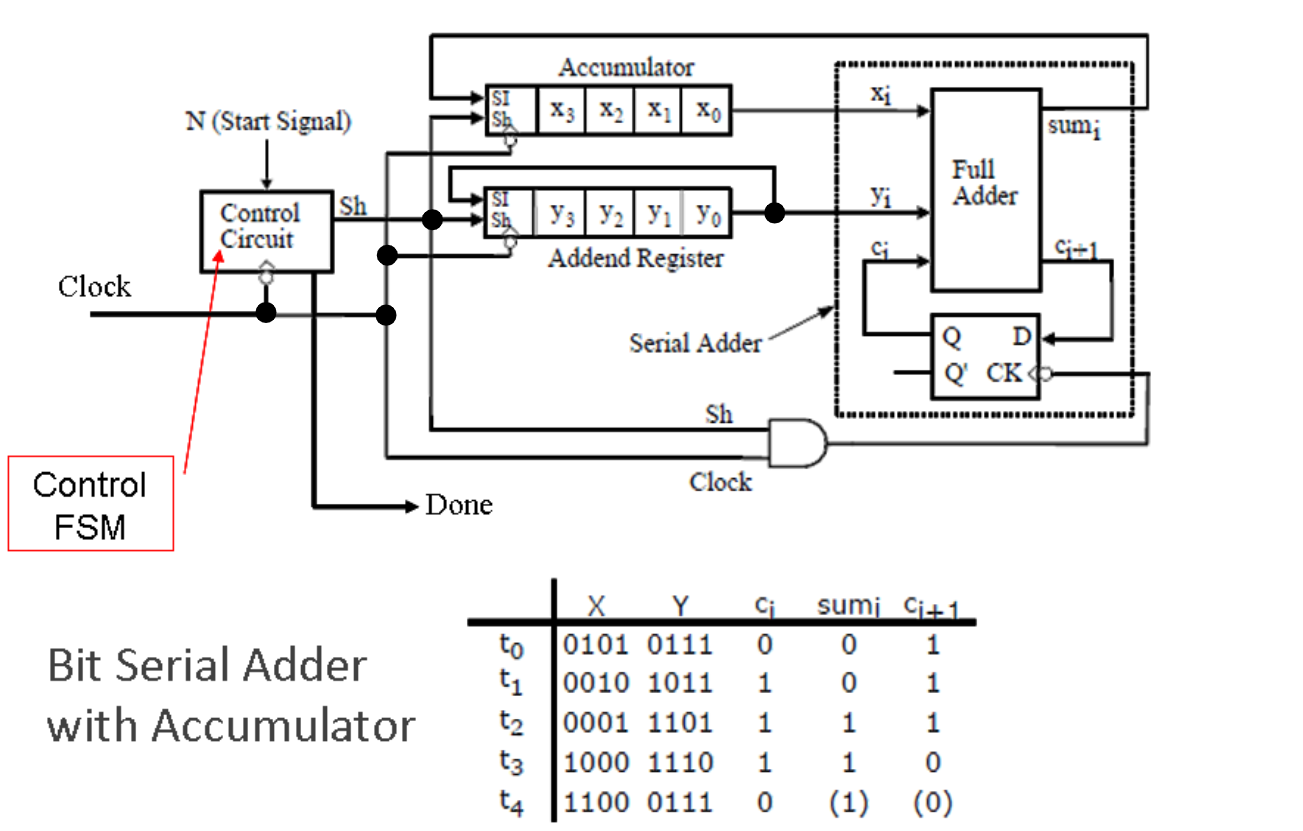
The above block diagram shows how a serial adder can be implemented.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
